#include<iostream.h>
main()
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++)
cout<<" "<<j;
cout<<endl;
}
}
Output:
C++ is the language Cfree is the compiler.. You are the Program User. I am the Programmar. ~Osaid Jamal
Monday, 21 April 2014
Saturday, 19 April 2014
Switch Case- Simple Program
#include<iostream> //programmarsarmy.blogspot.com
using namespace std;
main(){
int n;
cout<<"Enter any number between 1-6:";
cin>>n;
cout<<"You entered:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"Name of Students\n"
<<"================\n"
<<" 1- Usaid\n 2- Rahim\n 3- Rida\n 4- Aysha\n 5- Jannat\n 6- Imtiaz"
<<"\n================"<<endl<<endl;
if(n>0&&n<=10)
switch(n)
{
case 1:
cout<<n<<"= usaid "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<n<<"= rahim"<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 3:
cout<<n<<"= rida "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 4:
cout<<n<<"= ayesha "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 5:
cout<<n<<"= Jannat "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 6:
cout<<n<<"= Imtiaz "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
}
}
Output:
using namespace std;
main(){
int n;
cout<<"Enter any number between 1-6:";
cin>>n;
cout<<"You entered:"<<n<<endl;
cout<<"Name of Students\n"
<<"================\n"
<<" 1- Usaid\n 2- Rahim\n 3- Rida\n 4- Aysha\n 5- Jannat\n 6- Imtiaz"
<<"\n================"<<endl<<endl;
if(n>0&&n<=10)
switch(n)
{
case 1:
cout<<n<<"= usaid "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<n<<"= rahim"<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 3:
cout<<n<<"= rida "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 4:
cout<<n<<"= ayesha "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 5:
cout<<n<<"= Jannat "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
case 6:
cout<<n<<"= Imtiaz "<<endl;
cout<<"================"<<endl;
break;
}
}
Output:
Wednesday, 16 April 2014
Calculator Using Else if Statement - C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int number1,number2;
char op;
int answer, answer1, answer2, answer3;
cout << "Enter value of number1: ";
cin >> number1;
cout << "Chose your Operator:";
cout<<"Press1 for +, press2 for -, press3 for *, press4 for/"<<endl;
cin >> op;
cout << "Enter value of number2: ";
cin >> number2;
if (op == '1')
{answer = number1 + number2;
cout << "Answer: " << answer << endl;}
else if (op == '2')
{answer1 = number1 - number2;
cout << "Answer: " << answer1 << endl;}
else if(op == '3')
{answer2 = number1 * number2;
cout << "Answer: " << answer2 << endl;}
else if (op == '4')
{answer3 = number1 / number2;
cout << "Answer: " << answer3 << endl;}
return 0;
}
Output:
Nested If Statement+Logic Gates- Using C++
//Question is:
/*if gender is male and grade is 70 and above,display "goodboy";
/*if gender is male and grade is 70 and above,display "goodboy";
if gender is female and grade is 70 above, display "goodgirl";
but if grade is below 70 regardless of gender,display "badchild"; */
//Source Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int grade;
char gender;
cout<<"Gender Is:";
cin>>gender;
cout<<"Grade Is:";
cin>>grade;
if(gender =='M'||'m')
if(grade>=70)
cout<<"goodboy";
if(gender=='F'||'f')
if(grade>=70)
cout<<"\n goodgirl";
else
cout<<"\n badchild";
return 0;
}
Output:
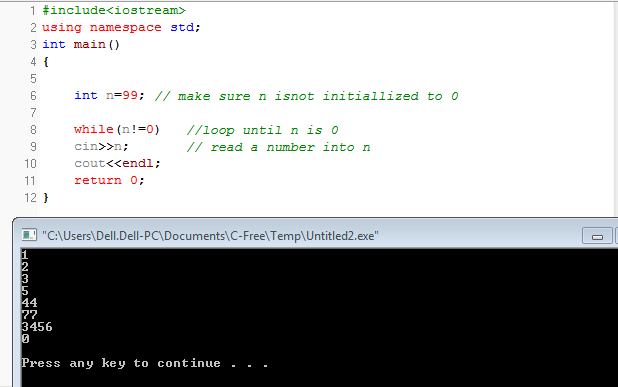
While Loop Basic Program1- Using C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n=99; // make sure n isnot initiallized to 0
while(n!=0) //loop until n is 0
cin>>n; // read a number into n
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n=99; // make sure n isnot initiallized to 0
while(n!=0) //loop until n is 0
cin>>n; // read a number into n
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
While Loop- Basic Program- Using C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=10;
while(a<20)
{
cout<<"value of a:" <<a <<endl;
a++;
}
}
Output:
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=10;
while(a<20)
{
cout<<"value of a:" <<a <<endl;
a++;
}
}
Output:
Compare Two Values- Relational Operators- Using C++
#include<iostream> // Including Header File
using namespace std; // C++ Program Standard
int main()
{
int num; // variable declaration
cout<<"Enter a number:"; // print enter a number :
cin>>num; // run time user input
cout<<"num < 10 is = "<< (num < 10) <<endl; // comparing no' s
cout<<"num > 10 is = "<< (num > 10) <<endl; // comparing no' s
cout<<"num == 10 is = "<< (num == 10) <<endl; //comparing no' s
}
Output:
using namespace std; // C++ Program Standard
int main()
{
int num; // variable declaration
cout<<"Enter a number:"; // print enter a number :
cin>>num; // run time user input
cout<<"num < 10 is = "<< (num < 10) <<endl; // comparing no' s
cout<<"num > 10 is = "<< (num > 10) <<endl; // comparing no' s
cout<<"num == 10 is = "<< (num == 10) <<endl; //comparing no' s
}
Output:
For loop Basic Program- Using C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "Hello" << "\n";
cout << "There" << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Output:
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "Hello" << "\n";
cout << "There" << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
Output:
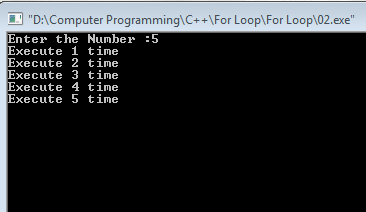
For Loop- Counter Program- Using C++
#include<iostream>
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Variable Declaration
int a;
// Get Input Value
cout<<"Enter the Number :";
cin>>a;
//for Loop Block
for (int counter = 1; counter <= a; counter++)
{
cout<<"Execute "<<counter<<" time"<<endl;
}
// Wait For Output Screen
getch();
return 0;
}
Output:
#include<conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Variable Declaration
int a;
// Get Input Value
cout<<"Enter the Number :";
cin>>a;
//for Loop Block
for (int counter = 1; counter <= a; counter++)
{
cout<<"Execute "<<counter<<" time"<<endl;
}
// Wait For Output Screen
getch();
return 0;
}
Output:
Factorial Using C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num,factorial=1;
cout<<" Enter Number To Find Its Factorial: ";
cin>>num;
for(int a=1;a<=num;a++)
{
factorial=factorial*a;
}
cout<<"Factorial of Given Number is ="<<factorial<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num,factorial=1;
cout<<" Enter Number To Find Its Factorial: ";
cin>>num;
for(int a=1;a<=num;a++)
{
factorial=factorial*a;
}
cout<<"Factorial of Given Number is ="<<factorial<<endl;
return 0;
}
Output:
Tuesday, 15 April 2014
Representation of a Linked List In a Memory
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *link;
};
node *head;
main()
{ head= new node;
head->data=405;
head->link=NULL;
cout<<"The Value in the starting node= "<<head->data<<endl;}
Output:
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int data;
node *link;
};
node *head;
main()
{ head= new node;
head->data=405;
head->link=NULL;
cout<<"The Value in the starting node= "<<head->data<<endl;}
Output:
Saturday, 12 April 2014
Array Using C++
Array: An array is a variable that holds multiple values of the same type.
Arrays and pointers have a special relationship as arrays use pointers to reference memory locations. Syntax is :
#include <iostream.h>
#include <iomanip.h> //we use this header file for set w OR Width
main()
{
int arr[ 10 ]; // its an integer type array of size 10
/*initialize elements of (array) i.e start with 0 and n-1 means 0to9
for sum using for loop*/
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
arr[ i ] = i + 100;
// i.e calculation 100 =0 + 100 to 109= 9+100
}
cout << "Array Members" << setw( 12 ) << "Values" << endl;
// again for loop for output/ display
for ( int j = 0; j < 10; j++ )
{
cout << setw( 6 )<< j << setw( 17 ) << arr[ j ] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Arrays and pointers have a special relationship as arrays use pointers to reference memory locations. Syntax is :
datatype arrayname[array size];
#include <iostream.h>
#include <iomanip.h> //we use this header file for set w OR Width
main()
{
int arr[ 10 ]; // its an integer type array of size 10
/*initialize elements of (array) i.e start with 0 and n-1 means 0to9
for sum using for loop*/
for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
{
arr[ i ] = i + 100;
// i.e calculation 100 =0 + 100 to 109= 9+100
}
cout << "Array Members" << setw( 12 ) << "Values" << endl;
// again for loop for output/ display
for ( int j = 0; j < 10; j++ )
{
cout << setw( 6 )<< j << setw( 17 ) << arr[ j ] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output:
Pointers Using C++ Program 1
//Pointers: A pointer is a variable that contains the address of a variable.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int x=100; // initialize integer type variable name x
int *y; // declare integer type pointer y
cout<<x; // print value of integer type variable x
cout<<"\n"; // new line
y=&x; // giving address of variable x to y
*y=5000; // without accessing x changing value of x=100 to 5000
cout<<x; // after, poiting now, value of x is : 5000
cout<<"\n"; // new line
int **z; // declare integer type pointer to pointer c
z=&y; // giving address of y to z
**z=90; // now, without disturbing x&y value of x is 90
cout<<x; //value of x is 90
}
Output:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int x=100; // initialize integer type variable name x
int *y; // declare integer type pointer y
cout<<x; // print value of integer type variable x
cout<<"\n"; // new line
y=&x; // giving address of variable x to y
*y=5000; // without accessing x changing value of x=100 to 5000
cout<<x; // after, poiting now, value of x is : 5000
cout<<"\n"; // new line
int **z; // declare integer type pointer to pointer c
z=&y; // giving address of y to z
**z=90; // now, without disturbing x&y value of x is 90
cout<<x; //value of x is 90
}
Output:
Nested For Loop Using C++ Program(2)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
main()
{
for(int i=1;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<i<<"\t";
for(int j=1;j<5;j++)
cout<<j;
cout<<"\n";
}
}
// پہلا لوپ ایک بار چلے گا تو دوسرا والا لوپ 4 بار چلے گا اور پھر پہلا والا لوپ دوسری بار چلے گا تو دوسرا
//لوپ 4 بار چلے گا پھر اسی طرح چار بار پہلا لوپ چلے گا
OutPut:
using namespace std;
main()
{
for(int i=1;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<i<<"\t";
for(int j=1;j<5;j++)
cout<<j;
cout<<"\n";
}
}
// پہلا لوپ ایک بار چلے گا تو دوسرا والا لوپ 4 بار چلے گا اور پھر پہلا والا لوپ دوسری بار چلے گا تو دوسرا
//لوپ 4 بار چلے گا پھر اسی طرح چار بار پہلا لوپ چلے گا
OutPut:
Fabonacci series Using C++
#include<iostream> // header file
using namespace std;
main() // simple main function
{
//variable declaration
int number, firstvalue = 0, secondvalue = 1, next ;
// simple programming of cout
cout<<"Enter the number of terms:\a";
cin>>number;
cout<<"-------------------------------------\n"<<endl;
cout<<"Fabonacci series of "<<number<<"is:\n";
cout<<"-------------------------------------\n"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<number;i++)
{
if(i<=1)
next = i;
else
{
next = firstvalue + secondvalue;
firstvalue = secondvalue;
secondvalue = next;
}
cout<<next<<"\t";
}
cout<<"\n\n \a";
}
// fb: programmarsarmy.blogspot.com
OutPut:
using namespace std;
main() // simple main function
{
//variable declaration
int number, firstvalue = 0, secondvalue = 1, next ;
// simple programming of cout
cout<<"Enter the number of terms:\a";
cin>>number;
cout<<"-------------------------------------\n"<<endl;
cout<<"Fabonacci series of "<<number<<"is:\n";
cout<<"-------------------------------------\n"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<number;i++)
{
if(i<=1)
next = i;
else
{
next = firstvalue + secondvalue;
firstvalue = secondvalue;
secondvalue = next;
}
cout<<next<<"\t";
}
cout<<"\n\n \a";
}
// fb: programmarsarmy.blogspot.com
OutPut:
Friday, 11 April 2014
00- How to print any message using c++ ?
#include<iostream> // including header file
using namespace std;
using namespace std;
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)